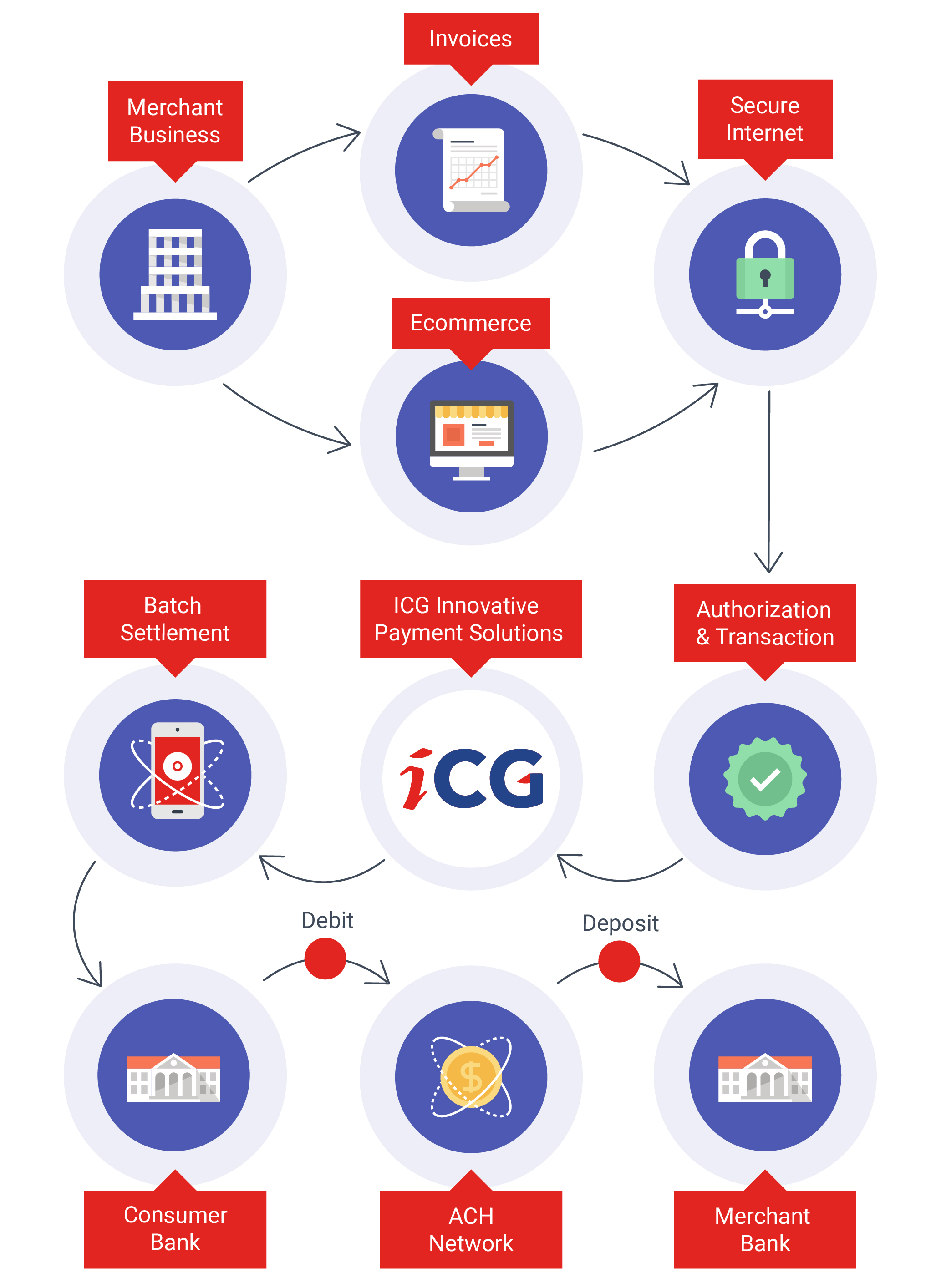
What is ACH Processing?
An ACH transaction starts with a Receiver authorizing an Originator to issue ACH debit or credit to an account. A Receiver is the account holder that grants the authorization. An Originator can be a person or a company (such as the gas company, a local cable company, or one's employer). Accounts are identifed by the bank's Routing Number and the Account Number within that bank.
In accordance with the rules and regulations of ACH, no financial institution may issue an ACH transaction (whether it be debit or credit) towards an account without prior authorization from the Receiver. Depending on the ACH transaction, the Originator must receive written (SEC Codes: ARC, POP, PPD), verbal (TEL), or electronic (WEB) authorization from the Receiver. Written authorization constitutes a signed form giving consent on the amount, date, or even frequency of the transaction. Verbal authorization needs to be either audio recorded or the Originator must send a receipt of the transaction details before or on the transaction date. An electronic authorization must include a customer being presented the terms of the agreement and typing or selecting some form of an "I agree" statement.
Once authorization is acquired, the Originator then creates an ACH entry to be given to an Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI), which can be any financial institution that does ACH origination. This ACH entry is then sent to an ACH Operator that passes it on to the Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI), where the Receiver's account is issued either a debit or credit.
The RDFI may, however, reject the ACH transaction and return it to the ODFI if, for example, the account had insufficient funds or the account holder indicated that the transaction was unauthorized. An RDFI has a prescribed amount of time in which to perform returns, ranging from 2 to 60 days from the receipt of the ACH transaction. However, the majority of returned transactions are completed within 24 hours from midnight of the day the RDFI receives the transaction.
An ODFI receiving a returned ACH entry may re-present the ACH entry two more times for settlement. Again, the RDFI may reject the transaction. After which, the ODFI may no longer represent the transaction via ACH.
ACH Applications
Process Electronic Checks and Credit Cards from within one Secure Internet-Based Tool from any computer with Internet Access for unlimited users!
Online Check Processing Reduces the hassle and delay of dealing with paper checks. Get your money faster and more manageably.
Recurring Billing by electronic ACH debits your customers bank accounts on an automatic schedule.
ACH Processing Funds are debited directly from your customer's bank account and deposited into yours. Fees for processing ACH checks online are considerably lower than those for processing credit cards.
Online Payments Accept ACH payments online through your ecommerce website or through your customer management or inventory application. Don't have a website or online invoicing application? We can build a custom system specifically tailored to your business needs.
Payment Security Industry standard SSL encrypted communication and multi-stage user credential authentication verification.
ACH Processing Entry Class Code Rules
ACH Processing Rules change from time to time. Each originator of ACH transactions is expected to know and follow the rules as determined by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA). This page is a high level summary of the Entry Class Codes used in iCheckGateway.com and is not intended to be all-inclusive of the rules.
PPD
Predetermined Payment & Deposit entries are contractual electronic payments or deposits to a consumer account.
Basic Rules - PPD
- - Electronic transactions must be authorized in writing.
- - Authorization must contain information about the amount and dates of the transaction(s).
- - Authorization must be maintained for two years and be made available to the receiving (check writer’s) bank within 10 banking days upon request.
CCD
Cash Concentration or Disbursement entries are contractual electronic payments or deposits to a corporate account.
Basic Rules - CCD
- - Electronic transactions must be authorized in writing.
- - Authorization must contain information about the amount and dates of the transaction(s).
- - Authorization must be maintained for two years and be made available to the receiving (check writer’s) bank within 10 banking days upon request.
TEL
Telephone Initiated entries are single entry electronic payments or deposits to a consumer account initiated by the consumer via telephone.
Basic Rules – TEL
- - These transactions must be authorized verbally and the authorization recorded or confirmation of the authorization may be sent to the customer via e-mail or regular mail. It is strongly encouraged that the merchant record all verbal authorizations in order to prove compliance.
- - Authorization must contain information about the amount and dates of the transaction(s).
- - Authorization must be maintained for two years and be made available to the receiving (check writer’s) bank within 10 banking days upon request.
Standard Entry Class (SEC) Codes:
ARC
Accounts Receivable Entry. A consumer check converted to a one-time ACH debit. The difference between ARC and POP is that ARC can result from a check mailed in where as POP is in-person.
BOC
Back Office Conversion. A single entry debit initiated at the point of purchase or at a manned bill payment location to transfer funds through conversion to an ACH debit entry during back office processing. Unlike ARC entries, BOC conversions require the customer to be present and a notice that checks may be converted to BOC ACH entries be posted.
CCD
Corporate Credit or Debit. Primarily used for business-to-business transactions.
CTX
Corporate Trade Exchange. Transactions that include ASC X12 or EDIFACT information.
DNE
Death Notification Entry. Issued by the federal government.
IAT
International ACH Transaction. This is a SEC Code for cross-border payment traffic. The code replaced the PBR and CBR codes as of September 18, 2009.
POP
Point-of-Purchase. A check presented in-person to a merchant for purchase is presented as an ACH entry instead of a physical check.
POS
Point-of-Sale. A debit at an electronic terminal initiated by use of a plastic card.
RCK
Represented Check Entries. A physical check that was presented but returned because of insufficient funds may be represented as an ACH entry.
TEL
Telephone Initiated-Entry. Verbal authorization by telephone to issue an ACH entry such as checks by phone. (TEL code allowed for inbound telephone orders only. NACHA disallows the use of this code for outbound telephone solicitations unless a prior business arrangement with the customer has been established.)
WEB
Web Initiated-Entry. Electronic authorization through the Internet to create an ACH entry.
XCK
Destroyed Check Entry. A physical check that was destroyed because of a disaster can be presented as an ACH entry.
ACH Return Codes
R01: Insufficient Funds
R02: Account Closed
R03: No Account/Unable to Locate Account
R04: Invalid Account Number
R05: Unauthorized Debit to Consumer Account Using Corporate SEC Code
R06: Returned per ODFIs Request
R07: Authorization Revoked by Customer
R08: Payment Stopped or Stop Payment on Item
R09: Uncollected Funds
R10: Customer Advises Originator is Not Known to Receiver and/or Originator is Not Authorized by Receiver to Debit Receiver’s Account
R11: Customer Advises Entry Not in Accordance with the Terms of the Authorization
R12: Account sold to another DFI
R13: Invalid ACH Routing Number
R14: Representative payee deceased or unable to continue in that capacity
R15: Beneficiary or Account Holder (Other Than a Representative Payee) Deceased
R16: Account Frozen
R17: Invalid Account Number Initiated under Questionable Circumstances/File Record Edit Criteria
R18: Improper effective entry date
R19: Amount field error
R20: Non-Transaction Account
R21: Invalid company identification
R22: Invalid individual ID number
R23: Credit entry refused by receiver
R24: Duplicate entry
R25: Addenda error
R26: Mandatory field error
R27: Trace number error
R28: Routing number check digit error
R29: Corporate customer advises not authorized
R30: RDFI not participant in check truncation program
R31: Permissible return entry
R32: RDFI non-settlement
R33: Return of XCK entry
R34: Limited participation DFI
R35: Return of improper debit entry
R36: Return of improper credit entry
R40: Return of ENR entry by Federal Government Agency (ENR Only)
R41: Invalid transaction code (ENR Only)
R42: Routing number/check digit error (ENR only)
R43: Invalid DFI account number (ENR only)
R44: Invalid individual ID number (ENR only)
R45: Invalid individual name/company name (ENR only)
R46: Invalid representative payee indicator (ENR only)
R47: Duplicate enrollment
R50: State Law Affecting RCK Acceptance
R51: Item is Ineligible, Notice Not Provided, Signature not genuine
R52: Stop Payment on Item
R61: Misrouted return
R62: Return of Erroneous or Reversing Debit
R63: Incorrect dollar amount
R64: Incorrect individual identification
R65: Incorrect transaction code
R66: Incorrect company identification
R67: Duplicate return
R68: Untimely Return
R69: Multiple Errors
R70: Permissible return entry not accepted
R71: Misrouted dishonored return
R72: Untimely dishonored return
R73: Timely original return
R74: Corrected return
R80: Cross-Border Payment Coding Error
R81: Non-Participant in Cross-Border Program
R82: Invalid Foreign Receiving DFI Identification
R83: Foreign Receiving DFI Unable to Settle
ACH Notification of Change (NOC) Codes
C01 - Incorrect bank account number: Bank account number incorrect or formatted incorrectly
C02 - Incorrect transit/routing number: Once valid transit/routing number must be changed
C03 - Incorrect transit/routing number and bank account number: Once valid transit/routing number must be changed and causes a change to bank account number structure
C04 - Bank account name change: Customer has changed name or ODFI submitted name incorrectly
C05 - Incorrect payment code: Entry posted to demand account should contain savings payment codes or vice versa
C06 - Incorrect bank account number and transit code: Bank account number must be changed and payment code should indicate posting to another account type (demand/savings)
C07 - Incorrect transit/routing number, bank account number and payment code: Changes required in three fields indicated
C09 - Incorrect individual ID number: Individual's ID number is incorrect
C10 - Incorrect company name: Company name is no longer valid and should be changed
C11 - Incorrect company identification: Company ID is no longer valid and should be changed
C12 - Incorrect company name and company ID: Both the company name and company id are no longer valid and must be changed
Check 21 Return Codes
RA: Not Sufficient Funds
RB: Uncollected Funds Hold
RC: Stop Payment
RD: Closed Account
RE: Unable to Locate Account
RF: Frozen/Blocked Account
RG: Stale Dated
RH: Post Dated
RI: Endorsement Missing
RJ: Endorsement Irregular
RK: Signature(s) Missing
RL: Signature(s) Irregular
RM: Non Cash Item
RN: Altered/Ficticious Item
RO: Unable to Process
RP: Item Exceeded Dollar Limit
RQ: Not Authorized
RR: Branch/Account Sold
RS: Refer to Maker
RT: Stop Payment Suspect
RU: Unusable Image
RV: Image Fails Security Check
RW: Cannot Determine Account
ACH Processing Terms
ABA NUMBER - See Routing/Transit Number.
ACH - An acronym used to identify the Automated Clearing House Network.
ACH AUTHORIZATION - Agreement by a receiver to allow an ACH credit or debit entry to its account. Authorizations for credit transactions may be oral, but consumer debit transactions must be authorized in writing or similarly authenticated by other means (e.g., by digital signature or PIN if by computer).
ACH CREDIT - A transaction through the ACH Network originated to pay a receiver (deposit into an account).
ACH DEBIT - A transaction through the ACH Network originated to remove funds from the receiver (withdrawal from an account).
ACH NETWORK - Funds transfer system governed by the rules of the National Automated Clearing House Association, which provides for the interbank clearing of electronic entries for participating financial institutions.
ACH OPERATOR - The ACH operator processes entries between an originator and receiver. There are currently two ACH operators -- the Federal Reserve Bank and EPN (Electronic Payments Network).
ACQUIRER - A financial institution or Merchant Service Provider (MSP) that facilitates and manages credit card processing on behalf of a merchant customer.
ACQUIRER BANK - The bank or financial institution that holds the merchant's bank account that is used for collecting the proceeds for credit card processing.
ACQUIRING PROCESSOR - The credit card processing entity with which an acquirer partners in order to provide merchants with transaction clearing, settlement, billing and reporting services.
ADDENDA RECORD - An ACH record type that carries supplemental data needed to completely identify an account holder(s) or provide information concerning a payment to the RDFI or receiver.
ANSI - The American National Standards Institute.
AUTHENTICATION - A critical data security technique used to prevent the alteration of data as the data are exchanged between the participants in an ACH transaction.
AUTOMATED DEPOSIT - A deposit made directly to an account at a DFI through the ACH network (i.e. payroll deposits, social security payments, and retirement benefits).
BANK IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (BIN) - A BIN is the first six digits of the credit card, debit card, charge card, etc. These digits identify which network the card belongs to as well as which bank issued it.
BANKING DAY - Any day on which a DFI is open to the public during any part of the day for carrying on substantially all its financial functions. With reference to ACH, any day on which the ACH operator is open and processing ACH transactions.
BATCH - A group of records or documents considered as a single unit for the purpose of data processing.
BUSINESS DAY - A day on which a financial institution is open and performing substantially all of it operations.
CLEARING HOUSE - A voluntary association of DFIs that facilitate the clearing of checks or electronic items through the direct exchange of funds between members.
COMMERCIALLY REASONABLE - A system, technology, practice or procedure frequently practiced among originators conducting similar types of business.
DATA ENCRYPTION STANDARD - A technique by which a message is scrambled into an indecipherable stream of bits for transmission.
DATA TRANSMISSION - The electronic exchange of information between two data processing points (computers).
DESCRIPTIVE STATEMENT - A bank account summary that contains information concerning one or more entries for which no separate item is enclosed. ACH entries necessitate some form of descriptive statement unless a substitute enclosure document is produced by the financial institution. Minimum reporting requirements are defined by Regulation E.
DFI - Depository Financial Institution.
DIRECT DEBIT - A method of ACH collection used where the debtor gives authorization to debit his or her account upon the receipt of an entry issued by a creditor.
EFFECTIVE ENTRY DATE - The date placed on an ACH transaction by the originator of the transaction or the ODFI - it is normally the date the originator or ODFI intends the transfer to take place.
ELECTRONIC FUNDS TRANSFER - A generic term used whenever money is moved without the use of a check or draft.
ELECTRONIC FUNDS TRANSFER ACT - The United States federal law that governs the use and administration of electronic funds transfer services.
ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES IN GLOBAL AND NATIONAL COMMERCE ACT (E-SIGN) - A United States federal law that defines and governs the use of digital signatures and records in electronic commerce.
FILE HEADER - The first record of an ACH file containing information necessary to route, validate and track the ACH transactions contained within the file.
FUNDS AVAILABILITY - The time at which funds associated with ACH, cash or check deposits are made available to the account holder.
INTERCHANGE - The process by which all parties involved in a credit card transaction (i.e., processors, acquirers, issuers, etc.) manage the processing, clearing and settlement of credit card transactions, including the assessment, collection and/or distribution of fees between parties. Also known as Credit Card Interchange.
ISSUING BANK - A financial institution that issues credit cards to consumers on behalf of the card associations. Also know as Card Issuing Bank or "Issuer."
MEMO POSTING - A notation posted to an account which indicates a credit has been received, but has not yet been posted to the account.
MERCHANT ACCOUNT - A financial institution or bank account that is used by a merchant specifically for the purpose of collecting proceeds consumer bank account or credit card payment transactions. A Card Present (CP) merchant account is used by merchants that receive payments in a physical location where payment is physically presented to the merchant by the customer at the time of the transaction. A Card Not Present (CNP) merchant account is where payment is not physically presented to the merchant by the consumer at the time of the transaction.
MERCHANT ACCOUNT PROVIDER - A financial institution or bank that provides a financial account to a merchant for the purpose of collecting proceeds from consumer bank account or credit card payment transactions.
MERCHANT IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (MID) - An identification number assigned to each member merchant of an acquiring organization, such as a financial institution, Independent Sales organization (ISO), Merchant Service Provider (MSP) or processor.
NACHA - (NATIONAL AUTOMATED CLEARING HOUSE ASSOCIATION) - A body which develops, maintains the NACHA Operating Rules and oversees all ACH activities and procedures. NACHA is also responsible for the sale and distribution of payment-related publications and providing national education.
NON-SUFFICIENT FUNDS - A type of ACH return indicating that a receiver's bank account does not have sufficient funds to cover a specific transaction.
NOTIFICATION OF CHANGE - Notification to a merchant from a receiver's bank indicating that bank account information provided with a specific transaction was incorrect and includes correct information.
ODFI (ORIGINATING DEPOSITORY FINANCIAL INSTITUTION) - A participating DFI which is responsible for the origination of ACH transactions. This institution may deposit items directly with an ACH operator or may work through a third-party processor which is the actual Sending Point.
ORIGINATOR - An organization or company that produces an ACH file and delivers it to an ODFI for introduction into the ACH Network.
PARTICIPATING DEPOSITORY FINANCIAL INSTITUTION - Any DFI that is authorized by the ACH operator to originate or receive ACH entries.
PAYMENTS GATEWAY - A system of technologies and processes that allow merchants to electronically submit payment transactions to the payment processing networks (i.e., the Credit Card Interchange and the ACH network). Payments Gateways also provide merchants with transaction management, reporting and billing services.
PRENOTIFICATION (PRENOTE) - A zero dollar entry that must be sent through the ACH Network at least six calendar days prior to any live entries affecting an account at a RDFI. The prenote allows the RDFI to validate entry information.
RECEIVER - A term used when referring to the clearing of ACH transaction to describe the person or corporate entity that has authorized an originator to initiate a refund or charge transaction to their bank account.
RDFI (RECEIVING DEPOSITORY FINANCIAL INSTITUTION) - A participating DFI which is responsible for the receipt of ACH transactions. This institution may receive items directly with an ACH operator or may work through a third-party processor which is the actual Receiving Point.
RECEIVING POINT - A processing site that receives entries from an ACH operator on behalf of an RDFI.
REGIONAL PAYMENTS ASSOCIATION - An organization formed by DFIs to regulate and support the exchange of electronic transactions.
REGULATION CC - This regulation, published by the Federal Reserve Bank Board of Governors, implements the Expedited Funds Availability Act and the Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act.
REGULATION E - This regulation, published by the Federal Reserve Bank Board, establishes the rights, liabilities and responsibilities of consumers who use electronic fund transfers and financial institutions that offer electronic fund transfer services.
RETURNED ITEM - An ACH entry that has been rejected by a RDFI because it cannot be posted (i.e. account closed, no account, NSF, etc.).
REVERSING ENTRY - A file created by a Sending Point to cancel a previous file or entry because the previous file or entry was sent in error or is a duplicate.
ROUTING/TRANSIT NUMBER - A nine-digit number, also known as the ABA number, which is used within the banking system to identify a financial institution. The number is used on items (checks, ACH transactions, etc.) that belong to a specific financial institution so that they can be routed through the banking system to the proper institution.
SENDING POINT - A processing site that sends entries to an ACH operator on behalf of an ODFI.
SETTLEMENT - The process of accounting for transactions processed through the ACH operator. Settlement occurs daily.
SETTLEMENT DATE - The day on which settlement occurs, i.e., funds actually change hands as a result of an ACH entry.
SIMILARLY AUTHENTICATED - An authentication standard that allows written and signed authorizations to be obtained in electronic form. To meet the requirement of "in writing," an electronic authorization must be viewable on a computer screen or other display method that will allow the consumer to be able to ready the authorization.
SOURCE DOCUMENT - A check or sharedraft used to create an ACH entry.
STANDARD ENTRY CLASS CODE (SEC) - A three character code within an ACH Company/Batch Header Record to identify the payment types contained within an ACH batch. (i.e. CCD, CIE, CTX, MTE, POS, WEB, or PPD).
THIRD-PARTY SENDER - A third-party service provider is considered to be a third-party sender when there exists an agreement with an ODFI or another third-party sender to originate transactions and also has an agreement with an originator to initiate transactions into the ACH Network on their behalf. In this situation, there is no agreement between the originator and the ODFI. A third-party sender is a subset of the third-party service provider.
THIRD-PARTY SERVICE PROVIDER - An originator, an ODFI, or an RDFI may use a third-party service provider during the process of originating or receiving ACH transactions. Third-party service providers can include data processors, correspondent banks, or financial institutions providing ACH services to other financial institutions.
UNIFORM COMMERCIAL CODE ARTICLE 4A (UCC 4A) - Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) is a comprehensive body of state law governing commercial transactions. Article 4A covers certain funds transfers, including ACH credit transactions not subject to the Electronic Funds Transfer Act.
UPIC (UNIVERSAL PAYMENT IDENTIFICATION CODE) - Developed by the Electronic Payments Network, the ACH business of The Clearing House Payments Co. L.L.C., a UPIC is a unique bank account identifier that allows companies to receive electronic payments without divulging their sensitive banking information. UPICs are for credits payments only and are portable from one institution to another.
WAREHOUSING - The ability of an ODFI to receive a file from an originator prior to the Effective Entry Date and hold it for release to the ACH operator or for a RDFI to receive entries ahead of the Settlement Date and hold them without posting until the Settlement Date.
WHOLESALE CREDIT - A credit transaction originated or received by a non-consumer; i.e. a credit transaction to a "business account."
